Creating content for a global audience used to mean waiting weeks for a human translator and paying thousands of dollars for multilingual versions of your content. Neural machine translation changed this completely. AI translation now processes entire sentences at once rather than word-by-word. It understands context, recognizes idioms, and adapts cultural nuance through deep learning—something earlier translation systems struggled with terribly.
Video content creators, marketers, and educators now use AI translation tools that do far more than just translate dialogue. These platforms generate subtitles, clone voices in multiple languages, and even synchronize lip movements so dubbed videos look natural. Vozo AI combines translation and comprehensive AI translation capabilities into a single integrated platform.
What Is AI in Language Translation Anyway?
AI in language translation converts text or speech from one language to another using neural networks trained on massive parallel corpora. Artificial intelligence translation systems like Google Neural Machine Translation (GNMT) launched in 2016 supporting 100+ languages. The technology relies on language models called Transformers introduced in 2017. These use self-attention mechanisms to process entire sentences simultaneously rather than word-by-word translation.
From Rule-Based Systems to Neural Networks
Machine translation origins trace to Warren Weaver’s 1949 memorandum proposing digital computers for natural language processing. The Georgetown-IBM experiment in 1954 demonstrated English-to-Russian translation using 250 words and 6 grammar rules. The 1966 ALPAC report slashed U.S. funding after slow progress, though SYSTRAN proved viable for military applications in the 1970s.
Statistical machine translation dominated from the 1990s through 2016 by analyzing bilingual corpora to calculate word alignment probabilities. AltaVista launched free web translation software via Babelfish in 1996, handling 500,000 daily requests by 1997. The 2003 DARPA competition won by Franz Josef Och advanced how AI translation works before he joined the Google Translate team as lead.
Sequence-to-sequence translation models by Sutskever and Cho in 2014 marked the neural breakthrough using recurrent neural networks. Transformer architecture by Vaswani in 2017 enabled parallelizable training, becoming the foundation for modern AI translation systems that translate text much faster than a human translator.
How Does Neural Machine Translation Work?
Neural machine translation operates through encoder-decoder architectures. The encoder processes source language input into numerical representations. The decoder generates target language output token by token. The encoder transforms sentences into dense vector embeddings capturing semantic meaning independent of word order.
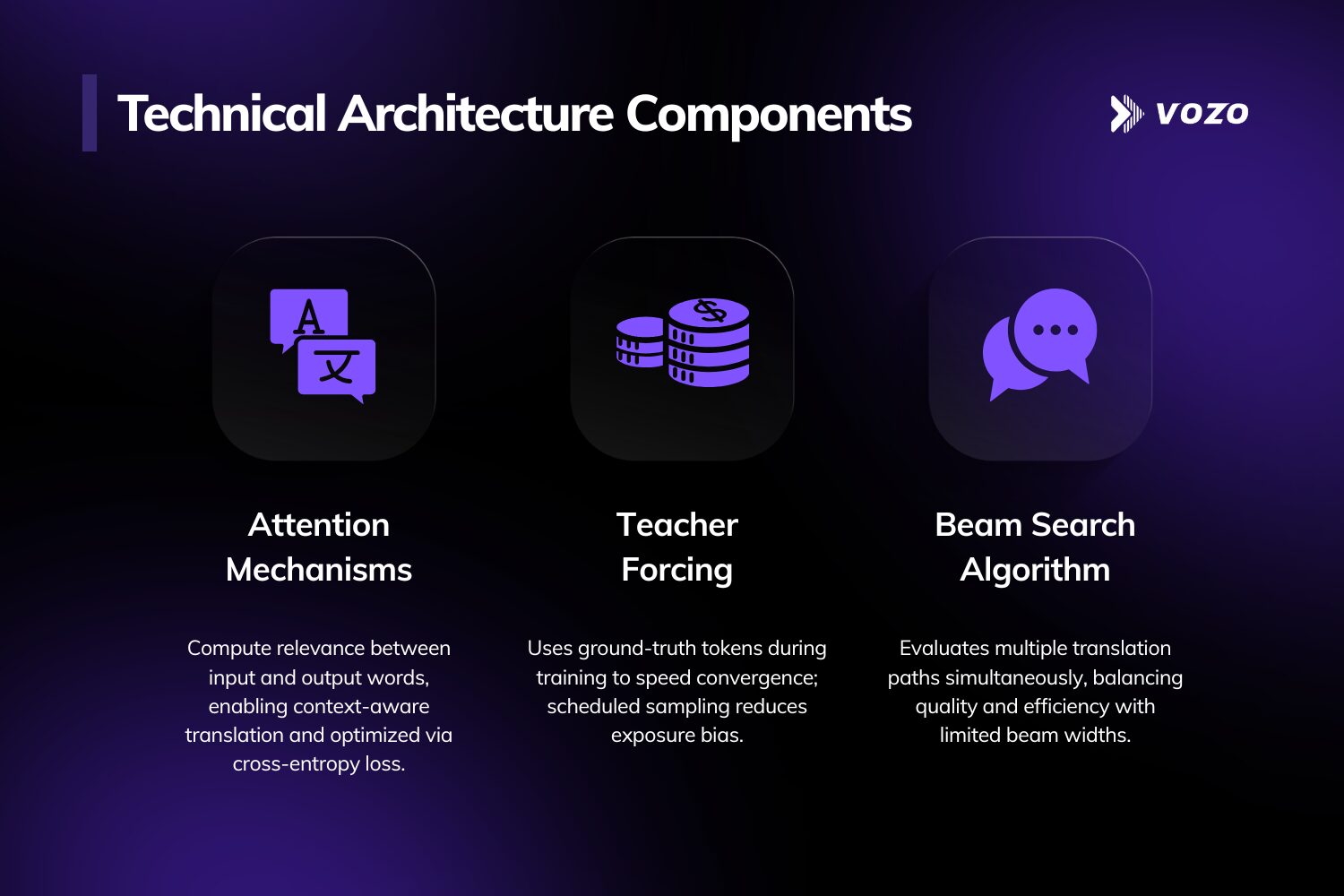
Technical Architecture Components
- Attention Mechanisms: Calculate relevance scores between each output word and every input word. This allows AI translation models to focus on appropriate context when translating ambiguous terms. The mathematical optimization follows cross-entropy loss functions: θ* = argmin_θ -Σ log P(y|x).
- Teacher Forcing: Feeds ground-truth tokens to the decoder during training phases, accelerating convergence. Production translation systems address exposure bias through scheduled sampling that gradually increases reliance on model-generated tokens.
- Beam Search Algorithm: Explores multiple translation candidates simultaneously rather than selecting the single highest-probability word at each step. Typical beam widths of 4-10 balance computational cost against translation quality.
Training requires approximately 100,000 sentence pairs for basic functionality. Production systems use billions of examples from datasets like Europarl. Document-level nmt extends these principles to process full texts, maintaining narrative consistency with error rates around 2.5 per 1,000 words in specialized content.
What Technologies Power Modern Translation Systems?
| Technology Type | Core Mechanism | Primary Use Cases | Performance Benchmark |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neural Machine Translation | Encoder-decoder with attention | General text, video subtitles | 2.5 errors/1,000 words |
| Statistical Machine Translation | Phrase-based probability models | Legacy systems | 5-8 errors/1,000 words |
| Rule-Based Machine Translation | Hand-coded grammar rules | Controlled domains | Consistent but inflexible |
| Post-Editing Machine Translation | AI draft + human refinement | Legal, medical, marketing | 50-70% of full cost |
| Large Language Models | Zero-shot prompting | High-resource pairs | Variable quality |
Neural machine translation dominates modern language translation through context-aware sentence processing. NMT systems use neural networks or Transformer architectures trained on parallel corpora. Redokun’s translation statistics indicate nmt replaced 65% of statistical systems between 2016-2020.
Hybrid Workflows and Post-Editing
Post-editing machine translation represents workflows where artificial intelligence generates draft translations. Human translators then refine for cultural appropriateness and domain terminology. This approach cuts translation projects timelines by 60-75% compared to full human translation work. Rates run 50-70% of full fees, making it viable for mid-budget translation services.
Generative AI and large language models like GPT-3 enable zero-shot translation through prompting without specialized training. These AI models achieve competitive results on high-resource pairs like English and Spanish but lag behind dedicated systems for low-resource languages. Translation technology continues advancing as using AI for translation becomes standard across the translation business.
Why Do Content Creators Use AI Translation Tools?
Content creators reach larger audiences by localizing videos across language barriers. YouTube’s algorithm prioritizes content in viewers’ preferred languages. The AI language translation market grows at 25% annually, driven by e-commerce and social media demands as AI is changing the way businesses communicate globally.
Industry-Specific Applications
- E-commerce Platforms: Product descriptions and customer reviews require translation across 10-15 languages. Real-time AI to translate enables customer support chat in multiple languages, helping businesses save time and cut translation costs significantly.
- Legal Services: Law firms use AI tools to mine datasets containing thousands of case documents. Globibo reports government adoption for transparency initiatives requiring public translation services accessible in minority languages.
- Educational Materials: Universities deploy automated translation for students accessing course materials in non-native languages. Computer-assisted translation helps translation teams maintain consistency across large volumes of educational content.
Vozo AI’s voice cloning analyzes source audio to replicate vocal characteristics—pitch, timbre, speaking pace, emotional inflection—in outputs. The platform’s lip synchronization adjusts mouth movements in video frames to match dubbed dialogue. Subtitle generation complements voice dubbing for accessibility, with smart line breaks matching speech patterns to help translate content effectively.
What Are AI Translation’s Technical Limitations?
Ai translation struggles with ambiguity, context-dependent meanings, and cultural references requiring deep background knowledge. Idioms confuse literal translation systems lacking pragmatic understanding of figurative language. Named entity transliteration fails when proper nouns require cultural adaptation.
Bias and Data Quality Challenges
The black box problem in neural networks obscures reasoning, making it impossible to trace why specific choices occurred. This amplifies bias risks when training data contains stereotypical associations. Non-standard speech patterns and code-switching degrade automatic speech recognition accuracy used in translation.
- Domain Shift Issues: Performance degrades when content diverges from training corpus composition. Medical terminology, legal jargon, or technical specifications require specialized AI model training or human oversight from a professional translator.
- Low-Resource Languages: Quechua, Hmong, and Punjabi lack sufficient parallel text for reliable training, creating divides where AI translation may concentrate benefits among well-documented languages.
- Numerical Precision Errors: Slight input variations yield divergent outputs. Version Internationale documented cases where legal translations inverted liability clauses or medical instructions reversed dosages, showing when the need for human translators remains critical.
Domain-specific training and human verification remain essential for high-stakes applications. Emerging techniques address limitations through transfer learning that leverages knowledge to bootstrap models for underrepresented languages.
Will AI Replace Translators in Professional Translation Work?
Translation technology shifts employment patterns rather than eliminating careers. CEPR research indicates 28,000 U.S. positions changed between 2010-2023. Bureau Works reports freelance earnings dropped 29.7% following ChatGPT 3.5 release as entry-level projects moved to AI handles basic tasks.
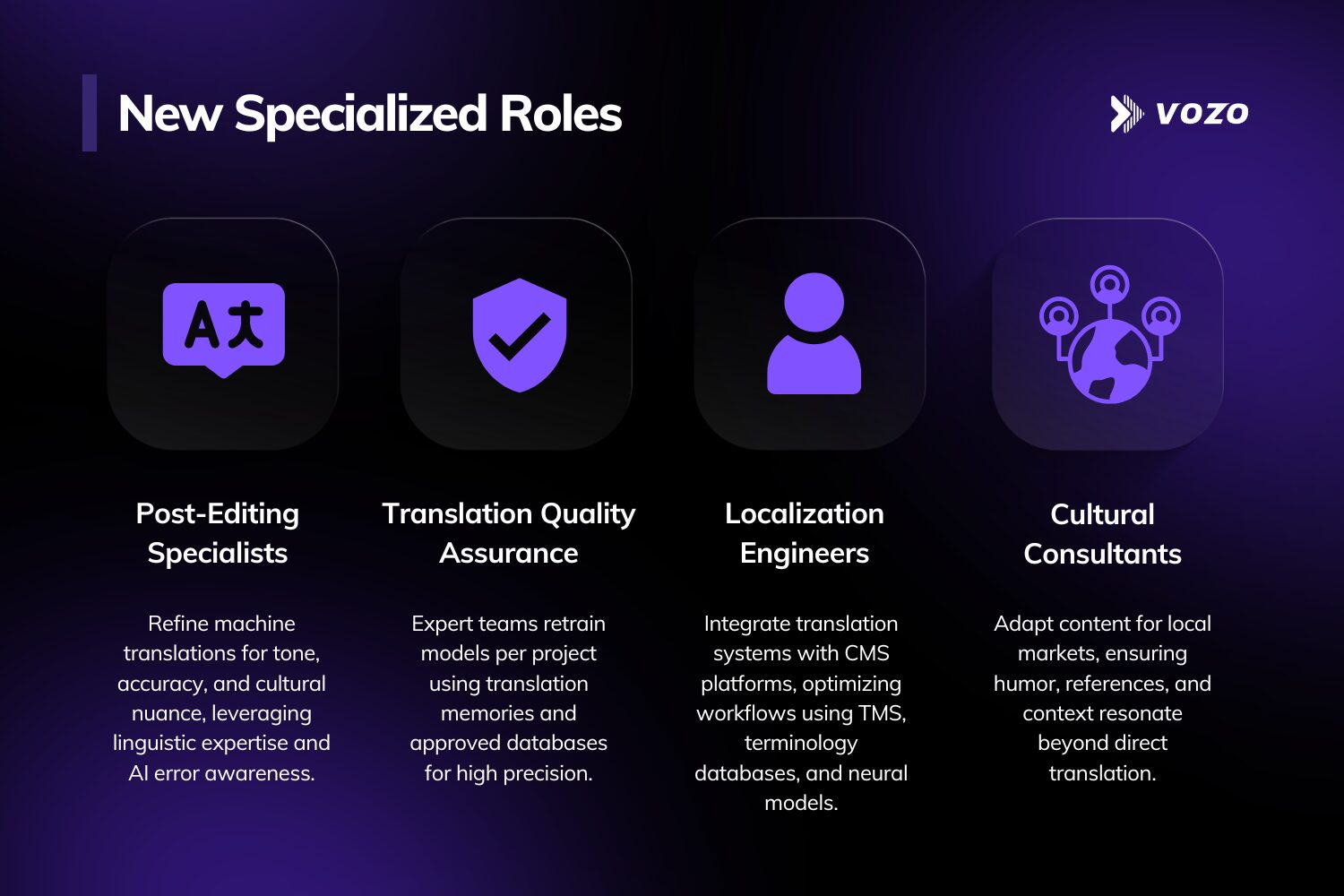
New Specialized Roles
- Post-Editing Specialists: Review and refine machine-generated outputs, focusing on cultural nuances and tone matching. These roles require linguistic expertise plus understanding of common AI strengths and error patterns.
- Translation Quality Assurance: Companies like LILT employ PhD-led teams that retrain models per project for precision using translation memories and approved translation databases.
- Localization Engineers: Bridge technical systems with content management platforms. These professionals optimize workflows integrating translation management systems, terminology databases, and neural models for localization and translation.
- Cultural Consultants: Advise on market-specific adaptations where direct translation fails. Gaming particularly relies on experts who adapt humor, references, and gameplay elements across language barriers.
The International Federation of Translators (FIT) represents 100+ associations and 80,000+ members across 55 countries. Training programs emphasize AI technology proficiency alongside linguistic skills, preparing professionals for hybrid human translation and AI translation workflows that show the advancement of AI reshaping the industry.
What Makes Video Translation Different?
Video translation requires integrated audio-visual synchronization beyond text translation. Speech recognition, neural machine translation, voice synthesis, and lip movement adjustments combine into cohesive experiences. Timing constraints demand translated dialogue fit within original duration windows.
Technical Requirements for Video Localization
- Voice Dubbing: Conveys emotion, urgency, humor through vocal tone and pitch variation. AI works to replicate paralinguistic features that text alone ignores using translation engines designed for audio processing.
- Lip Synchronization Technology: Modifies frames to adjust lip shapes, jaw movements, and facial expressions aligning with dubbed audio phonemes. Traditional manual sync required frame-by-frame analysis.
- Audio Source Separation: Isolates vocal frequencies from background music and ambient sounds. Vozo’s processing maintains production value by preserving background elements while swapping dialogue tracks, demonstrating AI translation uses for comprehensive video localization.
- Subtitle Constraints: Character limits of 42 per line impose compression. Reading speed considerations ensure viewers process subtitles before scene changes, requiring the translation process to balance accuracy with readability.
Systems like DeepL and Microsoft Translator focus primarily on text, while Vozo AI extends to complete video workflows. The platform handles translation models for audio-visual content, addressing how AI is changing the way creators approach global distribution and time to market optimization.
What Emerging Applications Show AI Translation Use Cases?
Ai translation extends beyond contemporary languages. Ancient language processing includes Akkadian cuneiform translation, helping archaeologists decode historical texts. Computer vision recognizes hand shapes for signed language translation between American Sign Language, British Sign Language, and national sign languages with distinct structures.
Real-time video translation emerges for live streaming, processing speech-to-translation-to-synthesis pipelines within 2-3 second latency. Multilingual models trained on code-switched text handle speakers alternating languages mid-sentence, reflecting bilingual communication patterns across common AI applications.
Transfer learning leverages high-resource knowledge to bootstrap models for Basque, Welsh, Hawaiian, and underrepresented languages. Document-level extends beyond sentences to maintain narrative consistency, preserving character voice in literature and argument flow in technical documentation. Translation agencies increasingly see how AI translation can benefit efficiency while maintaining quality through machine learning algorithms that improve with each translation project.
Top Video Translation Services
Ai and language translation technology transforms global content creation by making multilingual video production accessible. Neural machine translation, post-editing workflows, and specialized video localization deliver professional results. The technology’s evolution from 1954 Georgetown-IBM experiments to modern architectures processing 100 billion daily words demonstrates rapid advancement. Translation is used across industries to break down barriers and accelerate international expansion as new AI capabilities emerge.
Ready to reach global audiences with professional video translation services? Try Vozo AI’s platform to translate, dub, and synchronize your content—the system handles subtitle generation, voice cloning with authentic emotional delivery, and automated lip sync across multiple languages without requiring technical expertise from your translation team.
FAQs
Will AI replace translators completely in professional settings?
No, AI shifts translators toward specialized roles rather than eliminating careers. Complex creative content, legal agreements, and marketing campaigns requiring cultural adaptation demand human expertise for nuanced decision-making. The 28,000 U.S. position changes between 2010-2023 reflect role transformation toward post-editing, quality assurance, and cultural consultation where human judgment remains irreplaceable for high-stakes translation work.
Which systems perform best for technical documentation requiring precision?
Performance varies by language pair and domain specialization. Systems trained on domain-specific corpora outperform general models. Amazon leads machine translation likeness to human output per 2020 Intento benchmarks. LILT’s approach using teams that retrain models per project achieves high accuracy. Evaluation requires testing multiple systems against your specific content type, considering factors like terminology consistency and technical accuracy requirements.
Can Vozo AI handle real-time translation for live streaming applications?
Current capabilities focus on pre-recorded video translation, dubbing, and lip synchronization rather than real-time streaming. The platform processes uploaded videos through speech recognition, neural translation, voice synthesis, and lip sync adjustment workflows optimized for quality over latency. Real-time applications remain emerging technology requiring 2-3 second processing windows that comprehensive localization features don’t yet support for live broadcasts.
Back to Top: AI in Translation | How Neural Technology Reshapes Global Content Creation

